Published
Author: Mensah Alkebu-Lan
Table of Contents #
- Introduction
- Storage Devices for Data Storage
- Main Forms of Data Storage
- Disaster Recovery
- Tiered Storage
- References
Introduction #
Protecting your users’ and company’s important files and historical archive of documents with storage solutions is a vital part of running a business. In that case, it’s helpful to know what data storage options are available.
Storage Devices for Data Storage #
Flash storage is a solid-state technology using flash memory chips for writing and storing data. A solid-state disk (SSD) flash drive stores data using flash memory.
Cloud storage delivers a cost-effective, scalable alternative to storing files to on-premise hard drives or storage networks. By “cloud” storage we mean the cloud storage service provider is responsible for the data centers that house the servers.
Hybrid cloud storage combines private and public cloud elements.

Types of Cloud Data Storage #
File storage is a hierarchical storage methodology used to organize and store data. Examples of file storage are Dropbox and Google Drive. One of the advantages of cloud storage over a handheld flash drive is you don’t have to physically possess the device.
A quality file storage solution will provide features like secure access to files. It will allow you to store, share, and collaborate on files and folders. Some solutions will also allow you to sync your files across your devices so your files are accessible in real-time. File storage providers will generally have options available partly depending on the amount of storage space you need.
Block storage is a technology used to store data into blocks. The blocks are then stored as separate pieces, each with a unique identifier.
Object storage is a data storage architecture for storing large amounts of unstructured data. An example of object storage is Amazon S3.
Disaster Recovery #
Disaster recovery is an organization’s method of regaining access and functionality to its IT infrastructure in the event of a natural disaster or cyber attack. A variety of disaster recovery (dr) methods can be a part of a disaster recovery strategy.
A disaster recovery (dr) plan should be a part of your business continuity plan.
There are several types of disaster recovery. Let us list a few:
- Hot Site
- Cold Site
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
- Point-in-Time Copies
As a part of this plan, an organization should have a statement of goals outlining what the organization wants to achieve during or after a disaster. This should include a recovery time objective (rto) and recovery point objective (rpo). For example, the recovery point objective is the acceptable amount of data loss sustained as the result of a disaster.
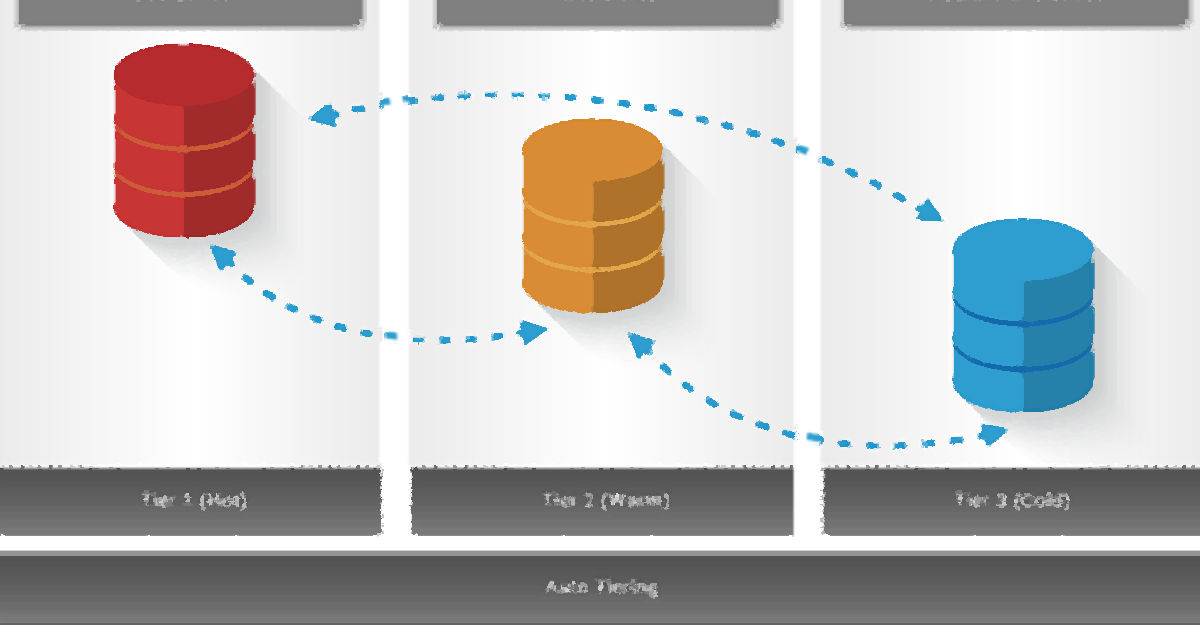
Tiered Storage #
Tiered storage, or tiered data storage, is a storage networking technique where data storage is carried out on various types of storage media based on price, performance, availability, and recovery attributes. It offers a sustainable long term solution for data management.
Tiered storage data classes include:
- Mission critical data – data required for high-performance applications
- Hot data
- Warm data
- Cold data
Both mission critical data and hot data is frequently accessed data. Once an organization is able to classify their data, the next step is to establish the actual storage tiers. In general, the higher the tier number, the “colder the data”, and by colder we mean the less frequently accessed. For example, in higher tires you may see technologies like tape storage systems being used.
The advantages of data tiering storage include:
- Reduced storage costs
- Increased Storage Efficiency
- Reusable storage equipment
- Improved disaster recovery
Organizations also have the option of automated storage tiering. We'll talk about that in the next article on this topic.

References #
- What is tiered Storage? Definition and related FAQs | Druva
- What Is Tiered Storage? - All You Need To Know About Tiered Storage
- Storage Tiering: Making the Most of Your Storage Investment - Cloudian
- Tiered Storage – Data Storage | Dell Technologies US
- What is data storage? | IBM
- What is Disaster Recovery? | VMware Glossary
- What is a Disaster Recovery Plan? Definition and Related FAQs | Druva
- What is Cloud Storage? | AWS